The Cornmill
THE EARLY HISTORY
The Luddenden Cornmills were owned by The Murgatroyd family for the majority of their life, the first record of a mill here was from 1274. There is a lot of published information about the early history of the mills (including Luddenden Mills), so there is no need to repeat this information here.
Grinding Corn was the earliest record for the use of water power in the Luddenden Valley, but there were many uses for this valuable resource. The valley had at least eleven water mills with a range of uses.
Wheat, Oats and Barley but no Corn
A Cornmill didn't actually grind Corn, well not Corn as we know it today as the word Corn is now used mainly to describe Maize. Historically Corn referred to all Cereal crops.
Here in the Pennines, the main cereal crop would have been Oats. Today when we think of Oats, we think of Scotland!.
Oats grow better than wheat in our cooler, wetter climate and heavy Pennine soil.
The locals tried long and hard to improve the quality of the soil here, bringing lime produced in the Yorkshire Dales and in Lancashire into the valley by packhorse to scatter on the fields to break up the clay soil.
The names of pack horse routes across the moors reflect this trade, Limers Gate for example is a track that runs across Midgley Moor over the summit of High Brown Knoll and down into Luddenden Dean.
Oats were used to make a flatbread know locally as Havercakes (derived the old Norse word for Oats, hafr). Fresh, these resemble a pancake but left to dry, they go hard and once dry, they store well.
Bread made from wheat flour would have been too expensive for the majority of people.
Stew and Hard was a local delicacy, the 'stew' being a slice of cold gelatinous cow heal stew as a filling and the 'hard' being a dry Havercake snapped in half and used like a slice of bread on either side of the stew.
BARLEY MALTING section to be added
THE CORNMILL AFTER 1854
The Last Days of Murgatroyd Control
The last Murgatroyds to run the mills were brothers Hartley (1797-1865) and John (1799-1873).
The brother's seem to have got into some financial difficulties and had to sell a lot of property in Luddenden and the surrounding valley including the Cornmills.
Twenty lots were put up for auction at the Murgatroyd Arms on 19th July 1854. Neither of the Mills sold on the day, but both change hands shortly afterwards.

The brochure for the auction included two maps, the first showed the lots for sale on the hills surrounding the village.
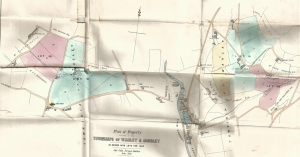
The second map shows the village lots.
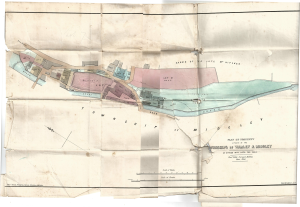
On this second map you can see the details so Lot 13, Upper mill includes the mill pond and a plot of land and sluices next to the weir. The land that the mill occupied is now housing (High Street Court).
The map shows the function of each of the buildings in the mill. The majority of the mill was being used for malting barley ready for making beer.
An accompanying document also describes the property;
All that valuable Corn Mill called "Upper Mill" situate in Luddenden, with the Malt Kiln, Warehouses, Stabling for 18 Horses, Wagon and Cart sheds, Gighouse, Joiner's Shop, Paved Yards and Outbuildings. Also the Reservoir behind the same, containing 2,008 superficial square yards, with the Water Wheel and the entire Fall of the Luddenden Brook, being about 30 horsepower. And also the Weir and Dam-stones across the Brook, Cloughs, and the Plot of Ground appropriate thereto, together with the use of the head Goit and the Tail Goits.' 'The Mill is five stories High, and attic, and the whole of the premises have been recently rearranged. The water wheel is a new iron one, 27 feet in diameter and nine on the breast.
Lot 14 was Lower mill. The three story building now know as The Cornmill is the only surviving part of the mill shown on this map. The two storey part of today's Cornmill was a later addition (but built before 1890. It can be clearly seen on the OS map published in 1894). Again you can see details of the use of the buildings.
You can see the head and tail goits that fed the water wheel and there is a boiler room and a chimney (so this mill had steam power at this date). There are cottages to the south side of the mill (Earlier documents show that these cottages were originally Oat drying houses, you can't grind wet grain!). [1])
'wherein Oates have and now are dryed and made ready to grind.... now converted into two dwelling houses or cottages on the south side of the Milne
and there is a building labelled 'Counting House' (probably a place to settle your bill or to pay your mulcture tax) adjacent to the bridge.
Some of the writing on the map is not clear on the scanned copy displayed in this document, but it is clearly readable on the original.
The land of Lot 14 is labelled as 'Holme' and it extends as far as the next weir on the brook. This whole area is now occupied by Blue Bell Walk. The field above Lower Mill, Lot 15 is labelled as 'Bank'. The Eastwood family bought both Lot 14 and 15 in about 1856 and immediately started to convert and extend this mill from a Corn Mill into a sizable woollen mill.
Below is a hand traced copy of the previous map, highlighting Lot 13. This copy is part of a document drawn up in 1856 when Upper Mill was sold by Hartley and John Murgatroyd to the Thompsons and their partner, Joseph Starkey (who bought a third share in the mill).
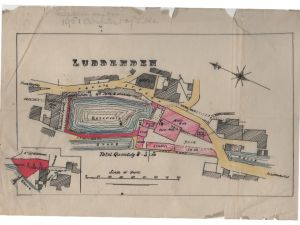
Upper Mill and The Thompson Family
In 1856, Upper Mill was Sold to:
- George Thompson (b.1786), one third share.
- Joseph Starkey, one third share.
- Robert Thompson (1810-1875), one sixth share.
- William Henry Thompson (b.1817), one sixth share.
Robert and William Henry Thompson were brothers.
George Thompson (b.1786), their father had an established Corn Milling business and already owned one of the Mills at Luddendenfoot. He was living at Middle foot in 1841.
Robert Thompson (1810-1875)
Robert Thompson was baptised at a Methodist Chapel in Luddenden on 13th August 1810. He was living at Upper Foot (this is the area around Burnley Road heading towards Brierley) in 1851 working as a Corn Miller. After the purchase of Upper Mill, Robert and his family moved into Chapel House (another Purchase in the 1854 Auction), the house that John Murgatroyd had lived in. At this stage he is employing 2 men according to the 1861 census.
In 1863, Robert bought William Henry's Share in the mill for £1000 (to become the sole owner of Upper Mill?)
By 1871, Robert and his family had moved to Carrfield (which was built for them?) and he is employing 11 men at Upper Mill.
Robert died in 1875 aged 65, his wife took ownership of the business which their son Arthur ran for her. The business continues to grow and in 1881 it employed 22 men and 2 boys.
But then, the family suffers some set backs, both of Robert and Hannah's sons died. George died in 1882 and Arthur the older son died in 1899. George's only son Frederick William died in 1894.
All of this is recorded on the family memorial in Luddenden Cemetery, the monument, a tall obelisk with a pink granite top is easily located and is situated to the north side of the chapel of rest.
This left the family with a big problem as there were no males left to succeed Arthur, so the Upper Mill passed to Robert's two daughters, Mary and Julia.
Whether through a fall in demand for milled oats and wheat or through a lack of leadership, the mill ceased to produce flour in the early 1890's and the Thompson sisters rented out sections of Upper Mill to people with new business ventures or for businesses requiring additional space for expansion. The mill in effect became an industrial estate.
William Henry Thompson (b.1817)
Meanwhile William Henry moves into Cooper House (in 1861 census) and then to Stansfield Hall (on John Naylor Lane, Luddendenfoot).
Having sold his share in Upper Mill, he concentrates his efforts on the family's other Cornmill at Luddendenfoot, Denholme Mill (on the south side of Burnley Road heading towards Cooperfield which overlooks the canal).
The family also owned one of the two mills at the bottom of Luddenden Brook as a Cornmill. These two mills were either side of the river, one roughly where the Weaver's Pub is situated, the one opposite on Mill Stream Drive. Perhaps they out grew this one and moved to Denholme Mill for more space (1854 OS Map: Luddendenfoot mills - one Cornmill, one Woollen mill. Denholme Mills - two Woollen Mills. 1894 OS Map: Luddendenfoot Mills - Two Woollen Mills. Denholme Mills, one Cornmill, one Woollen Mill)
The 1871 census shows that he is employing 16 men and 2 boys.

These invoices remind us that wheat was not the only cereal to be processed in the mill. The staple crop in the Pennines was Oats, not wheat, so what did the Cornmill produce?
The Thompson Family - Benefactors of Luddenden
To be completed
Luddendenfoot Methodist Chapel 1832.
United Methodist Free Church on Halifax Lane in 1837.
Luddendenfoot Congregational Savings Bank.
Donating land for the site of the Infant School on the corner of High Street and New Road.
Donating money towards a new road bridge Boy Bridge (1882) across the river Calder at Luddendenfoot (Luddendenfoot Local Board).
Lower Mill and The Eastwood Family
The Eastwoods were another of the mill owning families in the Luddenden Dean. They lived at Mill House on Railes Lane. The family were originally farmers. The brothers David, Eli Ogden, Henry, Samuel and Thomas picked up quiet a lot of the property auctioned by Hartley and John Murgatroyd in 1854.
They owned Pepper Mill on Duke Street and also Peel House Mill for some of it's life.
The Eastwood specialised in the manufacture of Woollen Blankets.
On acquiring Lower Mill, they leased the building out to another Woollen manufacturer Solomon Priestley and his son John Nicol Priestley (Solomon was originally a butcher as was his father).
By 1867, they had demolished the cottages originally used for drying oats and built a second shed and installed a second steam engine to power this new shed.
They, like all the other Mills in the valley, built a small Town gas plant (making gas from coal) presumably to provide lighting to the sheds. A small gasometer can be seen on the 1894 OS map roughly in the same position as the current electrical substation.
In 1873 they remortgaged all of the properties they bought from the Murgatroyds, plus their other mills and their home to raise £10,000. This would have been a substantial sum and equivalent to approximately £1 million today.
The OS map for 1894 shows that the footprint for the buildings at Lower Mill had more than doubled. One of these building can be seen in early photos of the mill, a second three storey building of a similar size to the one that has survived and presumably the one built by the Eastwoods in the 1860's.
There success did not last for long and the Eastwoods were bankrupted in 1879.
The Demise of The Cornmills
Industrialisation brought people to the valley, more than the local farmers could feed.
The Cornmills which were originally owned by the Lord of the Manor gradually slipped away from manorial control and new entrepreneurs took them over.
The improvement in the country's infrastructure and the arrival of steam power meant that wheat grown in more fertile soils could be cheaply transported into the Pennines in bulk and once here, no longer needed water power to convert it to flour.
The mills now needed to be close to canals and railways not close to streams and rivers. And as their output was no longer restrained by the quantity of water available, the mills could be bigger and became more centralised.
The trend continued, pushing the mills to ports like Hull, Liverpool and Manchester (thanks to the ship canal) as imported wheat became readily available.
This regionalisation, with areas of the country being dominant in one particular skill and dependant on other specialist hubs for the items they lacked has gown and now crosses national boundaries to become a global phenomenom!
The Pennine farmers no longer struggled to try and grow cereals and swapped to struggling to make a living out of cattle farming instead!
The old mills closed and were eventually demolished. A few buildings survived and were converted into apartments!!
